How Fast Can a Baby Die of Meningitis
Meningitis is a status that causes inflammation in the meninges, which protect the encephalon and spinal cord. Meningitis is nearly often caused by a virus or bacteria.
Meningitis is an uncommon merely potentially dangerous infection. Babies under 2 months of age are at greater gamble of getting meningitis, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP).
Experts are not sure why some babies get meningitis, but they believe it could be related to their immature immune systems.
Meningitis tin can have lasting effects on babies and tin can be fatal in some cases. However, prompt medical treatment can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications.

The symptoms of meningitis in babies may non be alarming at first. Some babies may just appear irritable or tired.
Meningitis can become serious speedily, and so information technology is essential to exist aware of its symptoms and to seek medical intendance immediately if meningitis is suspected.
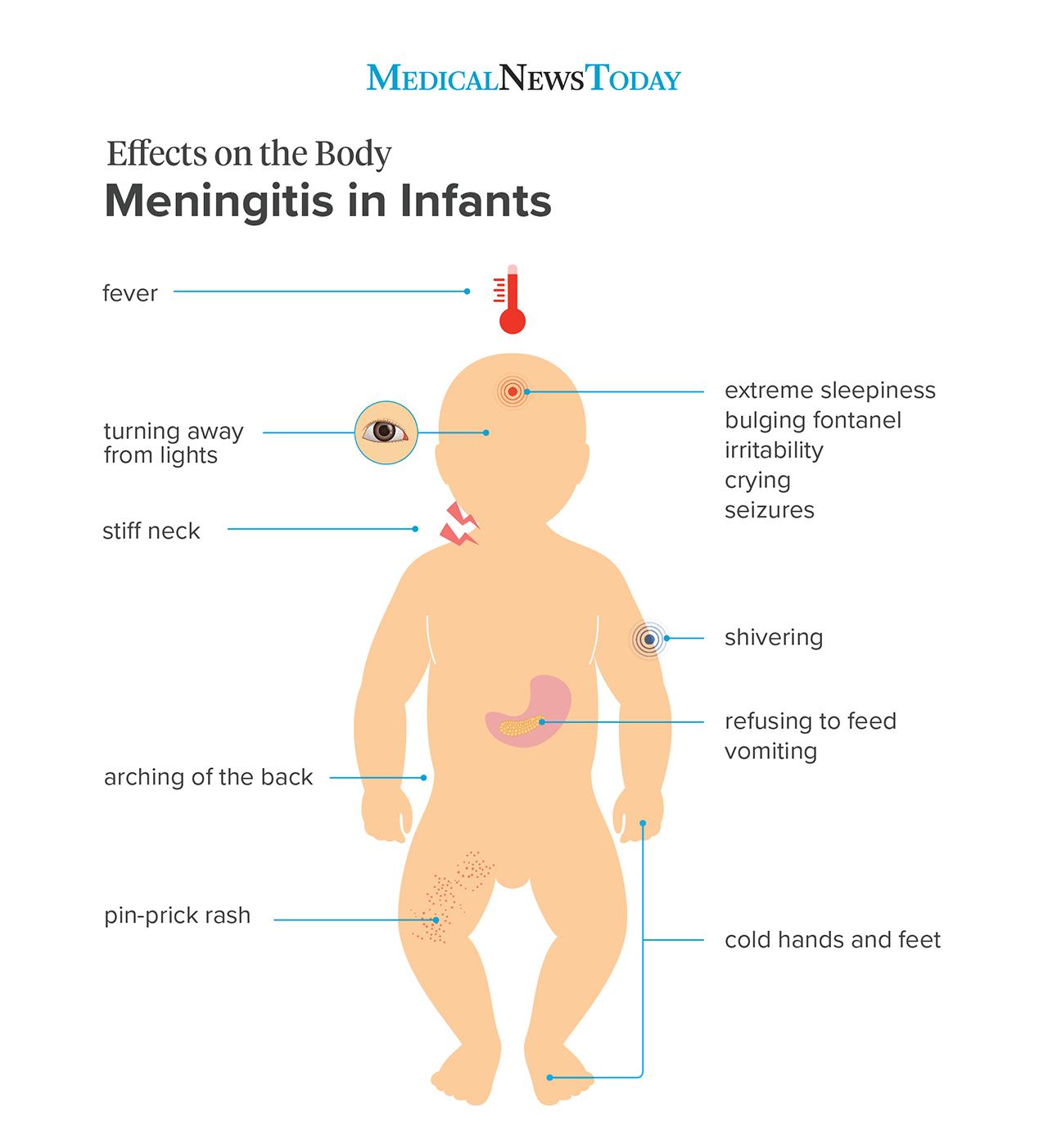
The nearly common symptoms of meningitis in babies include:
- Jutting fontanel (the soft spot on tiptop of the head). This may be due to increased pressure or fluid in the encephalon.
- Fever. A loftier temperature is a red flag for an infection, but some babies, peculiarly those under iii months of age, may not have a fever.
- Common cold hands and feet with a warm trunk.
- Chills. This may include shivering or chills, with or without a fever.
- A potent neck. Babies may hold their bodies in a stiff position and may concord their head tilted back.
- Irritability and crying, especially when picked up. This could be due to a sore or stiff neck or muscle and body aches.
- Rapid breathing.
- Vomiting persistently.
- Refusing to feed.
- Extreme sleepiness. A person may have difficulty with or be unable to wake the infant.
- Carmine or dark rash or marks on the body. If a baby has a fever, appears ill, and develops a rash, seek medical intendance correct abroad.
Babies that take whatever symptoms that could be meningitis should get emergency medical care. Prompt and aggressive handling helps ensure a better outcome.
Epitome credit: Stephen Kelly, 2019
The most common causes of meningitis in babies are bacteria and viruses. Bacterial meningitis is typically more dangerous than viral meningitis, though both require prompt medical care.
Several unlike viruses can crusade viral meningitis. They include:
- Non-polio enteroviruses. These are the nigh common cause of viral meningitis in the United states. They are oft spread through contact with an infected person'due south stool, saliva, or secretions from the eyes and nose. Infection with these viruses is common, but nigh people only develop a mild illness.
- Influenza. Influenza or the flu can be specially serious in babies, every bit information technology may lead to meningitis. Information technology is spread through coughing, sneezing, and close contact with an infected person.
- Canker simplex viruses (HSV). These viruses cause cold sores and genital herpes. According to the
World Health Organization (WHO), more than 65 percent of the world's population has HSV, and many practise not know it. A person tin can spread HSV to a baby through kissing, even when they have no symptoms. Newborns can contract HSV from their mothers during nascence. - Varicella-zoster virus. This virus causes chickenpox and shingles. It is highly contagious and usually spreads through breathing, talking, or contact with an infected person'south blisters.
- Measles and mumps. These diseases are extremely contagious and are spread through talking, coughing, sneezing, and sharing items, such every bit cups. Measles and mumps are less common since vaccines were introduced but are even so very serious in babies.
- West Nile virus or other viruses spread by mosquitoes.
About of these viruses will not crusade meningitis in a good for you person. Even so, babies are at a higher risk of meningitis and other complications, so protecting them from these illnesses is vital.
Causes of bacterial meningitis
Bacterial meningitis tin can be acquired by several different types of leaner. The most common types that infect babies include:
- Group B streptococcus , known as group B strep. This is passed from female parent to newborn during labor and childbirth if the mother is infected and not treated.
- Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is likewise spread from mother to baby during labor and birth and by eating contaminated nutrient.
- Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), which are commonly spread through coughing and sneezing.
- Listeria monocytogenes , which is spread through contaminated food. A fetus can be infected with listeria during pregnancy if the female parent consumes food contaminated with the leaner.
- Neisseria meningitidis , which is spread through saliva.
Bacterial meningitis is treated with antibiotics that are typically given intravenously in the infirmary through an IV.
According to the AAP, almost babies who receive prompt antibiotic treatment will recover completely. Even so, well-nigh 20 percent may be left with lifelong effects, including hearing problems, learning disabilities, seizures, and paralysis.
Viral meningitis does not respond to antibiotics. It is usually not as serious as bacterial meningitis (except for HSV in newborns), and many babies will recover completely without complications.
Nonetheless, both types of meningitis require prompt medical attending. Babies may need extra hydration with IV fluids, pain relief, monitoring, and rest in club to make a full recovery.
Meningitis can be spread easily from person to person. Although information technology cannot be prevented completely, some precautions can significantly reduce the take chances of a infant getting it.
Vaccines are fundamental
Babies should receive vaccines as outlined past the
Although vaccines practise not forbid all cases of meningitis, they help protect against several types of serious bacterial and viral meningitis. This greatly reduces the run a risk of a baby getting the illness.
Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b) vaccine
Earlier the Hib vaccine was bachelor, this leaner was the leading cause of bacterial meningitis. Today, infection with Hib has become much less common due to the vaccine.
Hib vaccine is given at 2, 4, and half dozen months of age, and once more between 12 and xv months of age. Hib vaccine is given either solitary or in a combination vaccine.
Pneumococcal vaccine
Pneumococcus bacteria can cause meningitis and other serious infections, such as pneumonia. The pneumococcal vaccine is typically given at 2, 4, and 6 months of age, followed past a final dose between 12 and fifteen months of age.
Children with sure wellness conditions may get an additional dose between 2 and 5 years of age.
Meningococcal vaccine
The most common type of meningococcal vaccine is known as the meningococcal cohabit vaccine (MCV4 or
MMR vaccine
The MMR vaccine protects against measles, mumps, and rubella. Before this vaccine became available, mumps was a common cause of viral meningitis, specially in babies and children. Measles tin can also cause meningitis.
The MMR vaccine is given at 12 to 15 months of age and again at 4 through half dozen years of age.
Newborns accept not yet received all their vaccines, and their immune systems take not adult fully. Therefore, it is ofttimes advised to avoid people and places that may expose a baby to higher amounts of germs. Assist protect babies from meningitis and other illnesses with these tips:
- People who have common cold sores or who are decumbent to cold sores should avoid kissing babies.
- Keep babies away from people who are sick or who are coughing, sneezing, or not feeling well.
- Keep the infant away from big crowds of people whenever possible.
- Wash hands before preparing food or bottles for a baby.
- Ask others to wash their hands before holding the babe and to avoid touching the baby's face.
- Pregnant women should get a group B strep exam between 35 and 37 weeks of pregnancy. Mothers who exam positive for group B strep should receive antibiotics during labor to forestall spreading the infection to the baby.
- Go along babies indoors during prime mosquito activity. This is usually from dusk until dawn. If the babe must exist outside, employ long sleeves, long pants, and ask a pediatrician virtually safe mosquito repellants.
As well, do not expose babies to cigarette smoke, which may increase the risk of getting viral or bacterial illnesses, such equally meningitis.
Meningitis symptoms tin come on quickly and apace become serious in babies. For this reason, babies should exist given emergency medical intendance if whatsoever symptoms of meningitis appear, or if the infant'southward behavior is unusual.
Extreme fussiness without obvious crusade, a fever, excessive sleepiness, or a rash should exist checked by a dr. immediately.
Although meningitis can be serious, nearly babies will recover from viral or bacterial meningitis with proper medical intendance.
Source: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321033
0 Response to "How Fast Can a Baby Die of Meningitis"
Post a Comment